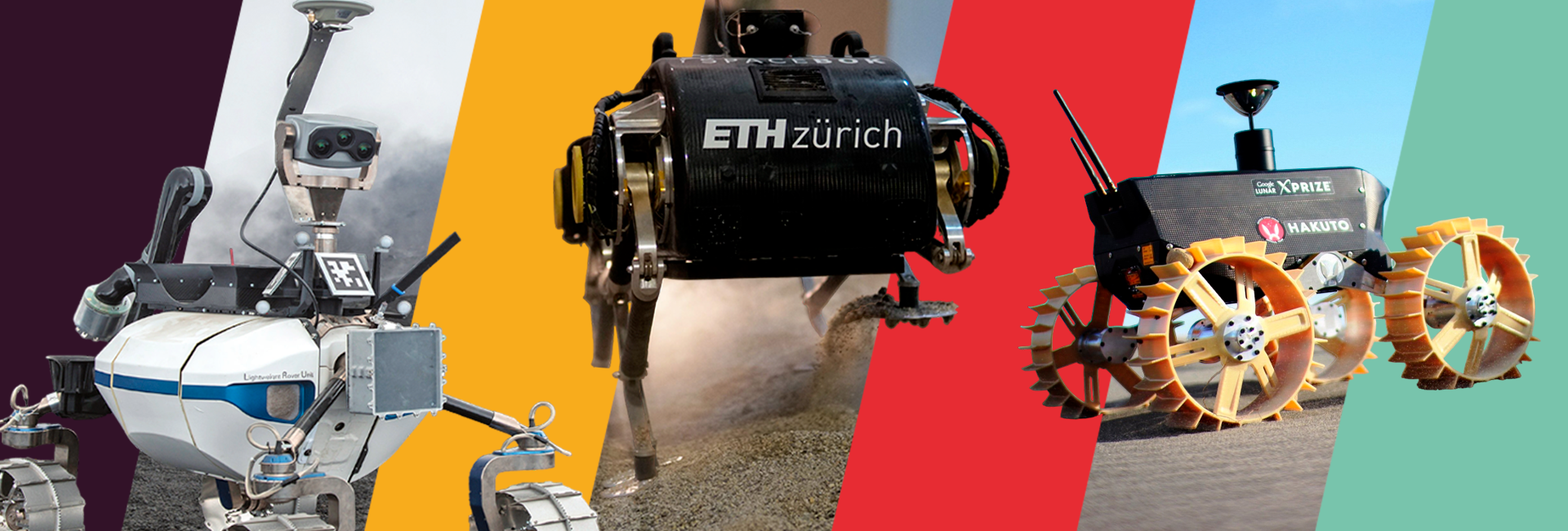
Robotics, and in particular multi-agent systems, can influence the way science and exploration are conducted in some of the most daunting and limiting environments on Earth and beyond. From the European Green Deal to NASA’s Artemis Program, having access to quality data from some of the most remote, yet significant, locations at large scales has become essential.
HERMES is an international working group founded in 2022 as a platform for exchanging ideas and fostering collaborations between researchers, scientists, and professionals interested in the subject of Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Cooperation for Exploration and Science in Extreme Environments (aka HERMES).
Currently, the working group is formed by 15 members from the following institutions:
Hermes is focused on :
- Status of and challenges in performing science and exploration in extreme environments, including but not limited to oceans, glaciers, arctic regions, volcanoes, hot springs, caves, underground tunnels, planetary surfaces, and asteroids.
- Study of immediate needs and scientific priorities for the deployment of heterogeneous multi-robot teams for Earth and Space.
- Recent findings and developments in the fields of multi-agent robot localization, mapping, coordination, communication, task planning, sampling, cooperative sensing, learning and decision-making.
- Presentation of novel mobile robotic concepts and prototypes for the exploration of unconstructed, dynamic environments.
- Dissemination of lessons learned from the development and field testing of heterogeneous multi-robot teams.
- Exploration of commercial ventures in the field of multi-robot cooperation for Earth and Space.
Worshop HERMES :
Abstract:
Despite promising developments in robotics and automation, we are reliant on humans and single-agent systems for some of the most dangerous scientific tasks on Earth and beyond. Environmental monitoring and sampling of rivers, oceans, and glaciers, spatio-temporal mapping of arctic regions, the characterization of off-Earth planetary environments, and the realization of space-based astronomy, are but some examples. Heterogeneous teams of robots have the potential to adapt to and thrive in these extreme, unstructured, and dynamic environments. Understanding the mechanisms by which teams of robots can be successfully deployed and autonomously cooperate to assist, augment, and eventually alleviate the need for large groups of humans in these regions is at the forefront of today’s robotics research and technology development. This workshop will bring together a community of roboticists, environmental scientists, machine learning experts, and space researchers with the goal of redefining the state of the art in the field of heterogeneous multi-robot cooperation for exploration and science in extreme environments.
Gallery :
Resources :
In the frame of HERMES, a set of downloadable resources is at your disposal below. You may use it for your presentations or written documents.